- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Driving Business Efficiency through Divisions and Departments
Driving Business Efficiency through Divisions and Departments
In case of a multi-divisional organizational structure, there is one parent company, or head-office. And that parent owns smaller departments, under the same brand name. Dividing the firm, into several self-contained, autonomous units, provides the optimal level of centralization, in a company.
What do we mean by a department or a division, in context of organizational structures?
The divisions are nothing, but distinct parts, of the same business.
A division of a business or "business division" is one of the parts, into which a business, organization, or company is divided.
Divisions are self-contained units.
The divisional structure consists of self-contained divisions.
Divisions can be defined for different business areas, research units, or administrative offices.
They might have different appointed managers.
And, Divisions may have programmatic, operational, fiscal and budgetary responsibility, for a specific set of business activities, and projects
What is the Relationship between, legal entity and divisions?
A department or division can be viewed as the intersection between a legal entity and a business unit.
In a simplistic scenario, all divisions are part of the same company.
The company itself is legally responsible, for all of the obligations and debts of the divisions.
However, this relationship, may change, in case of large organizations.
In that case, a business division may include, one or many subsidiaries as well.
Initially, in such companies, business units which are part of the same legal entity, are setup to operate in divisions.
Later with growth, these divisions become subsidiaries, and also independent legal entities.
In such cases, various parts of the business may be run by different subsidiaries.
Each subsidiary in such a case is a separate legal entity, owned by the primary business, or by another subsidiary in the hierarchy.
Divisions are also used by management, as a tool for segregation and delegation of responsibilities, to various parts of the business.
Divisions also help the management, in operational control.
Let us understand how they help management in these objectives.
Department as a tool for, Segregation & Delegation.
In case of a multi-divisional organizational structure, there is one parent company, or head-office.
And that parent owns smaller departments, under the same brand name.
Dividing the firm, into several self-contained, autonomous units, provides the optimal level of centralization, in a company.
Although, the whole organization is controlled by central management.
But most decisions are left to autonomous divisions or departments.
Central management provides the overall direction of the firm.
While each division operates autonomously to cater to its own needs.
It is held accountable for its own profits, and can remain productive, even if the other divisions fail.
Divisions as a tool for operational control
A division is a collection of functions, which manage similar types of activities, like the one which produce a product.
They are generally used as cost accumulators and also for revenue recognition.
They may have profit and loss responsibility, and may consist of a group of cost centers.
Departments can also serve as profit centers, managing their own profitability.
In that case, they utilize a budget plan to compete, and operate, as a separate business profit center.
What are some of the basis for creating divisions?
Divisional structure could be based on, many external or internal parameters, based on the management needs.
Some commonly used parameters across industry are, product, customer segment, geographical locations etc.
For example, in case of differentiation by products, each division is responsible for certain product, and has its own resources, such as finance, marketing, warehouse, maintenance etc.
Let us look at some common methods of differentiation, for creating divisions.
First could be, By Product; For example separate divisions are created, to manage different product or service lines.
Another way is to differentiate By Geographical Location; Example is the regional offices created by companies, like Northern Division, Southern division etc.
One can also define divisions by the Type of Customer; For example in case of a bank, different divisions are created to take care of retail business, wealth management and corporate clients.
And divisions can also be created by different Processes; for example in case of a hospital, one can have a division managing admissions, another for surgery, and one for discharge processes, etc.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Multitude of these legal and operational structures clubbed with accounting and reporting needs give rise to many reporting dimensions at which the organization may want to track or report its operational metrics and financial results. This is where business dimensions play a vital role.
-
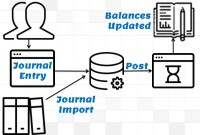
GL - Journal Posting and Balances
In this tutorial, we will explain what we mean by the posting process and what are the major differences between the posting process in the manual accounting system compared to the automated accounting systems and ERPs. This article also explains how posting also happens in subsidiary ledgers and subsequently that information is again posted to the general ledger.
-
A subsidiary is a company that is completely or partly owned by another corporation that owns more than half of the subsidiary's stock, and which normally acts as a holding corporation which at least partly or wholly controls the activities and policies of the daughter corporation.
-
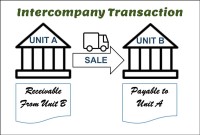
After reading this article the learner should be able to understand the meaning of intercompany and different types of intercompany transactions that can occur. Understand why intercompany transactions are addressed when preparing consolidated financial statements, differentiate between upstream and downstream intercompany transactions, and understand the concept of intercompany reconciliations.
-
Team-Based Organizational Structure
Team-based structure is a relatively new structure that opposes the traditional hierarchical structure and it slowly gaining acceptance in the corporate world. In such a structure, employees come together as team in order to fulfill their tasks that serve a common goal.
-
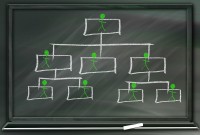
Divisional Organizational Structures
The divisional structure or product structure consists of self-contained divisions. A division is a collection of functions which produce a product. It also utilizes a plan to compete and operate as a separate business or profit center. Divisional structure is based on external or internal parameters like product /customer segment/ geographical location etc.
-
Legal Structures for Multinational Companies
A multinational company generally has offices and/or factories in different countries and a centralized head office where they coordinate global management. A multinational company (MNC)is a corporate organization that owns or controls the production of goods or services in at least one country other than its home country.
-
Operational Structures in Business
Large organizations grow through subsidiaries, joint ventures, multiple divisions and departments along with mergers and acquisitions. Leaders of these organizations typically want to analyze the business based on operational structures such as industries, functions, consumers, or product lines.
-
In this article we will focus on and understand the accounting process which enables the accounting system to provide the necessary information to business stakeholders. We will deep dive into each of the steps of accounting and will understand how to identify accounting transactions and the process for recording accounting information and transactions.
-
In this article, we explain some commonly used subsidiary ledgers like accounts receivable subsidiary ledger, accounts payable subsidiary ledger or creditors' subsidiary ledger, inventory subsidiary ledger, fixed assets subsidiary ledger, projects subsidiary ledger, work in progress subsidiary ledger, and cash receipts or payments subsidiary ledger.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved