- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Introduction to Organizational Structures
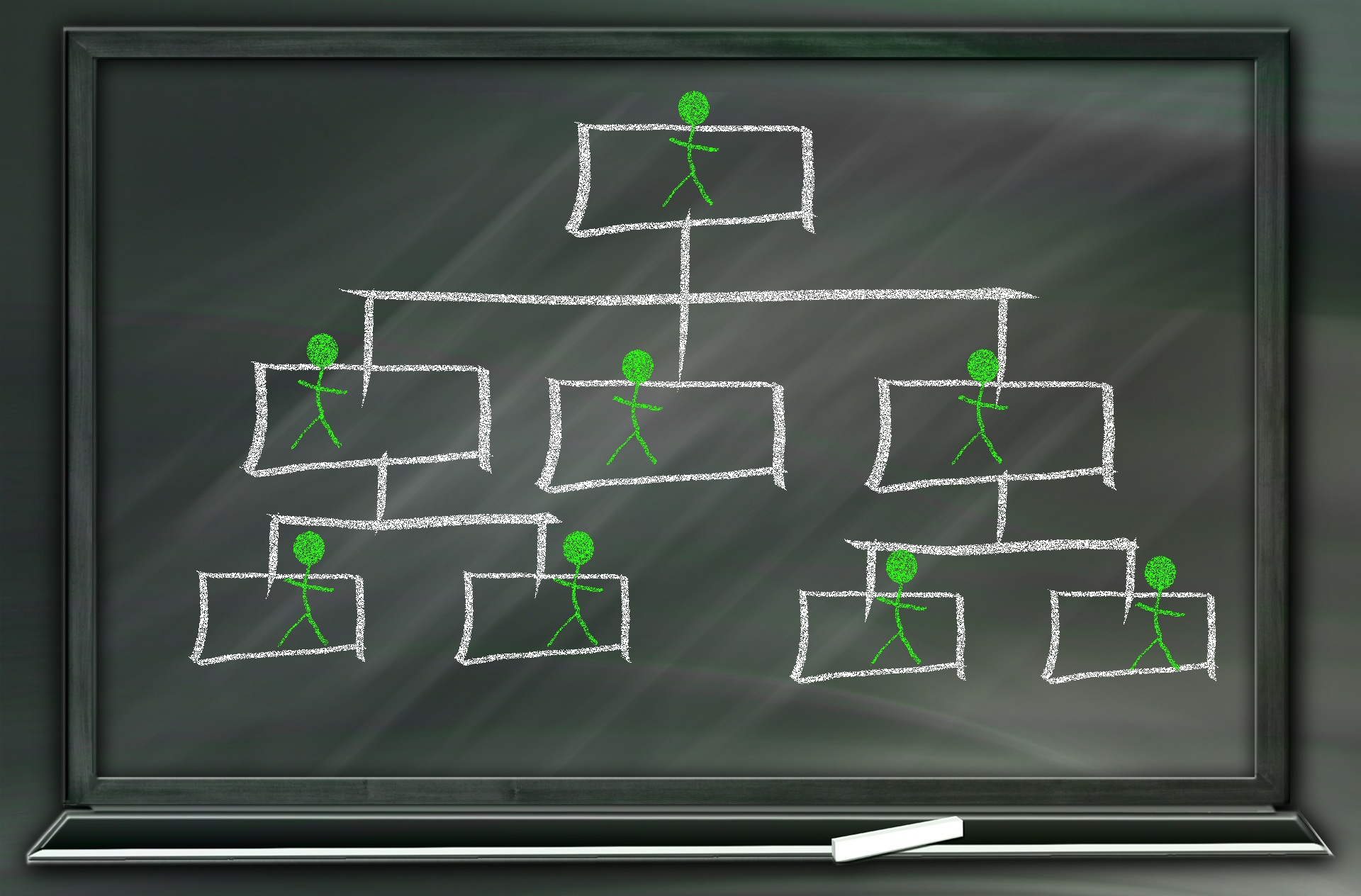
Introduction to Organizational Structures
Organizations are systems of some interacting components. Levitt (1965) sets out a basic framework for understanding organizations. This framework emphasizes four major internal components such as: task, people, technology, and structure. The task of the organization is its mission, purpose or goal for existence. The people are the human resources of the organization.
Organizations are systems of some interacting components. Levitt (1965) sets out a basic framework for understanding organizations. This framework emphasizes four major internal components such as: task, people, technology, and structure. The task of the organization is its mission, purpose or goal for existence. The people are the human resources of the organization.
What is an Organization?
The term organization is derived from the Greek word organon i.e., tool or instrument. It is often been understood as the embodiment of persistent efforts to coordinate, influence and control human behavior in order to reach some desired result. Organizations as Systems Organizations are systems of some interacting components. Levitt (1965) sets out a basic framework for understanding organizations. This framework emphasizes four major internal components such as: task, people, technology, and structure. The task of the organization is its mission, purpose or goal for existence. The people are the human resources of the organization. The technology is the wide range of tools, knowledge and/or techniques used to transform the inputs into outputs. The structure is how work is designed at the micro level, as well as how departments, divisions and the overall organization are designed at the macro level.
In addition to these major internal components of the organization as a system, there is organizations' task environment, such as suppliers, customers, and regulators. In simpler terms it is that part of external environment which is relevant at present or expected in foreseeable future to the organizations' goal attainment (Thompson, 1967).
Features of Organization
Max Weber has defined the following features and dimensions as basic for all organizations:
1. The organization has transparent and definite boundaries and has a collective identity of its own.
2. The organization has a central coordination system to manage the concentrated efforts of the organization
3. The organization is differentiated internally and decisions are implemented by a disciplined, specialized, continuously and rationally operating staff.
4. The organization is legitimate and organizational order, including the distribution of authority, power and responsibilities, is legitimate.
5. The organization's characteristics establish what is achieved and there is a high degree of steadiness between organizational goals, structures, processes, behavior and outcomes.
6. The organization is flexible and are deliberately structured and restructured in order to improve their problem solving capacity and their ability to realize predetermined goals.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Different Types of Organizational Structures
Modern business organizations run multiple product and service lines, operate globally, leverage large number of registered legal entities, and operate through complex matrix relationships. To stay competitive in the current global business environment, they must often develop highly diverse and complex organizational structures that cross international borders.
-
The purpose of the general ledger is to sort transaction information into meaningful categories and charts of accounts. The general ledger sorts information from the general journal and converts them into account balances and this process converts data into information, necessary to prepare financial statements. This article explains what a general ledger is and some of its major functionalities.
-
GL - Accrued / Unbilled Revenue
Accrued revenues (also called accrued assets) are revenues already earned but not yet paid by the customer or posted to the general ledger. Understand what we mean by the terms accrued revenue, accrued assets, and unbilled revenue. Explore the business conditions that require recognition of accrued revenue in the books of accounts and some industries where this practice is prevalent.
-
In this article, we will describe how to determine if an account needs adjustment entries due to the application of the matching concept. Learners will get a thorough understanding of the adjustment process and the nature of the adjustment entries. We will discuss the four types of adjustments resulting from unearned revenue, prepaid expenses, accrued expenses, and accrued revenue.
-
What Is a General Ledger? General Ledger (also known in accounting as the GL or the Nominal Ledger) is at the heart of any accounting system. A general ledger is the master set of accounts that summarize all transactions occurring within an entity. Ledger is the skillful grouping and presentation of the Journal entries. Learn the accounting fundamentals, general ledger process, and general ledger flow.
-
In this article, we will explain the general Ledger journal processing flow from entering journals to running the final financial reports. Understand the generic general ledger process flow as it happens in automated ERP systems. The accounting cycle explains the flow of converting raw accounting data to financial information whereas general ledger process flow explains how journals flow in the system.
-
In this article we will discuss various types of "Management Entities". Various types of operational units, are created by management, to effectively run, manage and control their business. Different types of functional units, and divisional units, are widely used across industry.
-
The general ledger is the central repository of all accounting information in an automated accounting world. Summarized data from various sub-ledgers are posted to GL that eventually helps in the creation of financial reports. Read more to understand the role and benefits of an effective general ledger system in automated accounting systems and ERPs.
-
Funds contributed by owners in any business are different from all other types of funds. Equity is the residual value of the business enterprise that belongs to the owners or shareholders. The funds contributed by outsiders other than owners that are payable to them in the future. Liabilities are generally classified as Short Term (Current) and Long Term Liabilities. Current liabilities are debts payable within one year.
-
Legal Structures for Multinational Companies
A multinational company generally has offices and/or factories in different countries and a centralized head office where they coordinate global management. A multinational company (MNC)is a corporate organization that owns or controls the production of goods or services in at least one country other than its home country.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved